Want to listen instead?
🔄 The Intricate Path of Glucose: From Insulin Release to Cellular Energy 💡
Introduction
- Cell signaling is a remarkable process that governs how our bodies maintain homeostasis, especially when it comes to glucose management. Every bite of food we take starts a cascade of signals that communicate with different organs, orchestrating the release of insulin and allowing our cells to take up glucose. This sophisticated mechanism is vital for energy production in the form of ATP, which fuels every function of our body.
- In today’s blog, provided by Mindful Diabetes Inc. as part of the “Pathways to Wellness” series, we will dive deep into this signaling process. We’ll explore how food communicates with the brain, leading to insulin release, and eventually triggering glucose uptake and energy generation. Finally, we’ll uncover how artificial sweeteners trick this process, leading to potential metabolic confusion and health concerns.
- Let’s unravel this pathway from the first taste of food all the way to cellular energy production!
❤️ Join Us in Preventing Type 3 Diabetes
Your gift supports scientifically backed prevention programs, cognitive-health education, and AI tools that help families reduce the risk of Alzheimer’s-like symptoms linked to diabetes.
Mindful Diabetes Inc. is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit — all donations are fully tax-deductible.
Tongue to Brain Signaling: The Gustatory Gateway
How Taste Buds Trigger Brain Responses
The process begins when food enters the mouth, and the taste buds detect sweetness, signaling the brain to prepare for glucose intake:
- Taste receptors on the tongue identify sweet flavors, causing gustatory cells to send a signal via the cranial nerves to the brainstem.
- The brainstem relays this information to the hypothalamus, which controls hunger and energy balance, preparing the body for glucose metabolism.
- The vagus nerve also becomes activated, linking the brain’s signals to the digestive system.
Preparing the Digestive Tract for Glucose
This signal informs the body that food containing glucose is incoming:
- The brain signals the pancreas to prepare insulin release in anticipation of rising blood glucose levels.
- The digestive system begins to secrete enzymes necessary for carbohydrate digestion.
- Cephalic phase insulin release happens even before the glucose enters the bloodstream, as part of the anticipatory response.
🌟 Try Our Free Wellness Tools!
Set the high score in our Mindful Eating Game, explore JEIR, or dive deeper into the science behind our AI-driven prevention tools!
🤖 Try JEIR — Your AI Wellness Guide 🎮 Play the Mindful Eating Game 📘 Read About the Mindful Eating Game 🤖📘 Read About the AI Behind JEIRBrain to Pancreas: The Endocrine Signaling Link
Insulin’s Anticipatory Release
Once glucose enters the bloodstream, the pancreas plays its vital role:
- The brain signals the pancreas’s beta cells to release insulin, the hormone responsible for lowering blood sugar.
- This is known as endocrine signaling, where insulin is secreted into the bloodstream to regulate glucose.
The Importance of Timing
Insulin release needs to be perfectly timed:
- If insulin release happens too early or too late, the body struggles to regulate blood sugar.
- Dysregulation can lead to insulin resistance, a precursor to metabolic diseases like Type 2 diabetes.
Insulin Signaling and Intracellular Cascade
Insulin Binding to Receptors
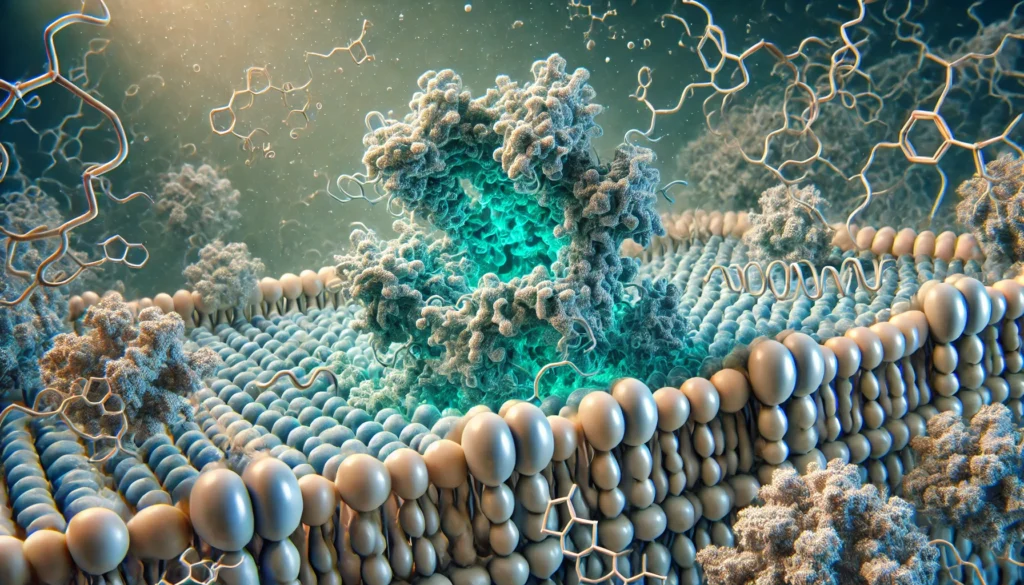
Once insulin is in circulation, it binds to its receptors on muscle, fat, and liver cells:
- Insulin receptors are proteins on the surface of these cells that recognize insulin and initiate the glucose uptake process.
- This binding triggers a cascade of signals within the cell, starting with the activation of insulin receptor substrates (IRS).
The Intracellular Signaling Cascade
The binding of insulin to its receptor sets off a series of reactions within the cell:
- Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K) is activated, which then leads to the activation of another molecule, AKT.
- These signals work together to move GLUT4 vesicles from inside the cell to the surface, where they can transport glucose into the cell.
Glucose Uptake & ATP Conversion: The Cellular Energy Factory
The Role of GLUT4
Once on the surface, GLUT4 transporters begin the crucial task of bringing glucose into the cell:
- GLUT4 acts as a gateway for glucose to enter muscle and fat cells.
- The more insulin is present, the more GLUT4 receptors move to the cell surface, enhancing glucose uptake.
From Glucose to ATP
Once inside the cell, glucose undergoes several metabolic processes:
- Glycolysis breaks down glucose into pyruvate, which enters the mitochondria for further processing.
- In the mitochondria, glucose is converted into ATP via oxidative phosphorylation, providing energy for cellular functions.
When This Process Goes Awry: The Impact of Artificial Sweeteners
How Artificial Sweeteners Disrupt Natural Signaling
Artificial sweeteners, such as aspartame or sucralose, can trick the body into thinking glucose is present:
- These substances bind to the same sweet receptors on the tongue, sending signals to the brain similar to those from real sugar.
- The body releases insulin in anticipation of glucose, but no glucose is delivered, leading to metabolic confusion.
The Long-Term Effects on Insulin Sensitivity
This repeated false signaling can have adverse effects:
- The body’s insulin response becomes blunted over time, contributing to insulin resistance.
- Without the actual glucose to process, the body may begin to store more fat, leading to weight gain and increased risk for Type 2 diabetes.
Conclusion:
- The journey of glucose from taste to cellular energy highlights the complexity and elegance of the body’s signaling mechanisms. However, when this intricate process is disrupted—such as by the use of artificial sweeteners—the body can be thrown into confusion, leading to metabolic disorders. Understanding the science behind these processes helps us appreciate the importance of natural glucose regulation.
- At Mindful Diabetes Inc., through our “Pathways to Wellness” series, we aim to provide insights into how you can maintain healthy glucose metabolism by making mindful choices, especially in your diet. Avoiding artificial sweeteners and focusing on whole, natural foods can help your body maintain balance and prevent disruptions in your insulin response.
📖 Continue Exploring 🌐
- Don’t stop here! Dive deeper into the fascinating connection between mental wellness and physical health in our upcoming blogs. There’s always more to discover and explore.
💌 Stay Informed and Inspired 📬
- Subscribe to our newsletter for the latest insights, tips, and updates on the mindful path to better health. Together, we’ll continue to unlock the secrets of a balanced and vibrant life.